
What is a Gear Reducer and How Does It Work?
A Gear Reducer is a vital component in many mechanical systems, allowing for precise speed reduction and torque multiplication. According to a recent market analysis by Smith Insights, the global gear reducer market is projected to reach $14 billion by 2025. This growth underscores the increasing reliance on these devices in various industries, from manufacturing to automotive.
Industry expert Dr. Jane Thompson, an authority on gear technology, explains, “Gear Reducers are essential for optimizing machinery performance.” This statement highlights the importance of these devices in enhancing efficiency and ensuring that equipment operates smoothly. However, not all gear reducers are created equal; choosing the wrong type can lead to suboptimal performance and increased wear.
Understanding how a Gear Reducer works is crucial. These components critically influence machine longevity and energy consumption. While many designs are effective, they are not foolproof. Users must be aware of their specific needs and applications. In these times of innovation, a poorly chosen Gear Reducer can hinder progress, emphasizing the need for careful selection and consideration in the design process.
What is a Gear Reducer?
A gear reducer, also known as a gear speed reducer, is a fundamental component in machinery. It helps to reduce the speed of a motor while increasing its torque. This two-fold function is essential for various applications in manufacturing and robotics. According to industry reports, nearly 40% of industrial energy consumption is attributed to motors. Gear reducers can optimize this energy usage.
In practical terms, gear reducers work by employing gears of different sizes. The smaller gear drives the larger gear, resulting in a lower output speed. For instance, a system that reduces speed by a ratio of 5:1 will generate five times more torque. This efficiency is crucial for heavy machinery, which often faces significant loads. As the Global Industry Analysts report, the market for gear reducers is expected to grow by 6.7% annually due to rising industrial automation needs.
However, choosing the right gear reducer can be challenging. A mismatched gearing ratio may lead to system inefficiencies and increased wear and tear. Some facilities overlook this detail, which can result in costly repairs. It's often wise to conduct an in-depth analysis of gear specifications and operational demands before making a decision. This careful consideration can yield better performance and extended equipment lifespan.
Principles of Gear Reduction
Gear reduction is a mechanical process that decreases speed while increasing torque. It takes place within a gear reducer, a device consisting of gears that work together. The primary principle here is simple: larger gears drive smaller gears. When a large gear turns, it moves the smaller gear, but at a reduced speed.
The gear reducer's efficiency comes from its ability to transform input speed into a more usable form of output. For instance, motor speed can be decreased to fit an application that requires more force. However, this reduction isn't always perfect; there can be losses due to friction and slippage. These inefficiencies remind designers to consider material and design choices.
Loading considerations add another layer to gear reduction. Too much load can lead to equipment failure. The design must ensure that the reducer can handle the expected loads without overheating or wearing out. It's crucial to balance speed and torque while assessing operational limits. Proper calculations are necessary to avoid potential problems, yet even experts can fall short at times.
What is a Gear Reducer and How Does It Work? - Principles of Gear Reduction
| Feature | Description | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gear Ratio | The ratio of the output speed to the input speed. | Increased torque, reduced speed. | Conveyor systems, robotics. |
| Types | Spur, helical, worm, planetary. | Variety for different applications. | Manufacturing, automotive. |
| Efficiency | Measures how much power is transmitted through the reducer. | Lower energy loss, better performance. | Industrial machinery, elevators. |
| Applications | Used in various machines to control speed and torque. | Versatile for multiple fields. | Wind turbines, printing presses. |
Components of a Gear Reducer
A gear reducer is an essential device in many mechanical systems. Its primary function is to decrease the speed of a motor while increasing torque. This is crucial in applications requiring high power transmission efficiency. Understanding its components helps in grasping its operation and importance.
Key components of a gear reducer include gears, casing, bearings, and input/output shafts. Gears are typically made from steel or plastic. They mesh together to provide the necessary speed reduction. The quality of the gears affects performance significantly. Bearings support shafts and reduce friction. Improper selection can lead to failures. The casing protects internal components from dust and damage.
In a recent industry report, it was shown that improper gear reducer installation increases downtime by about 20%. The bearings should also be regularly checked. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced lifespan. Additionally, selecting the wrong gear ratio can hamper efficiency. It's essential to balance torque and speed for optimal operation. These aspects highlight the complexity of gear reducers and the need for meticulous attention to detail.
Applications of Gear Reducers in Various Industries
Gear reducers play a crucial role in numerous industries. They effectively decrease the speed of motors, converting high-speed input into lower-speed output. This is especially important in conveyor systems, where precise movement is key. The reliable torque provided by gear reducers allows for the seamless transport of various materials.
In manufacturing, gear reducers ensure consistent performance. They are vital for robotic applications, helping to control the speed and force of robotic arms. These systems often rely on feedback loops that can be affected by gear design. In some cases, manufacturers face challenges when the gear reducers do not deliver expected efficiency. It's crucial to analyze load conditions and adjust the gearing appropriately.
In construction, heavy machinery utilizes gear reducers extensively. They enable cranes and excavators to operate smoothly under heavy loads. However, wear and tear on gears can lead to unexpected breakdowns. Industries must regularly assess gear health to avoid costly downtimes. Adapting to issues and learning from failures can improve overall performance.
Applications of Gear Reducers in Various Industries
Advantages of Using Gear Reducers in Mechanical Systems
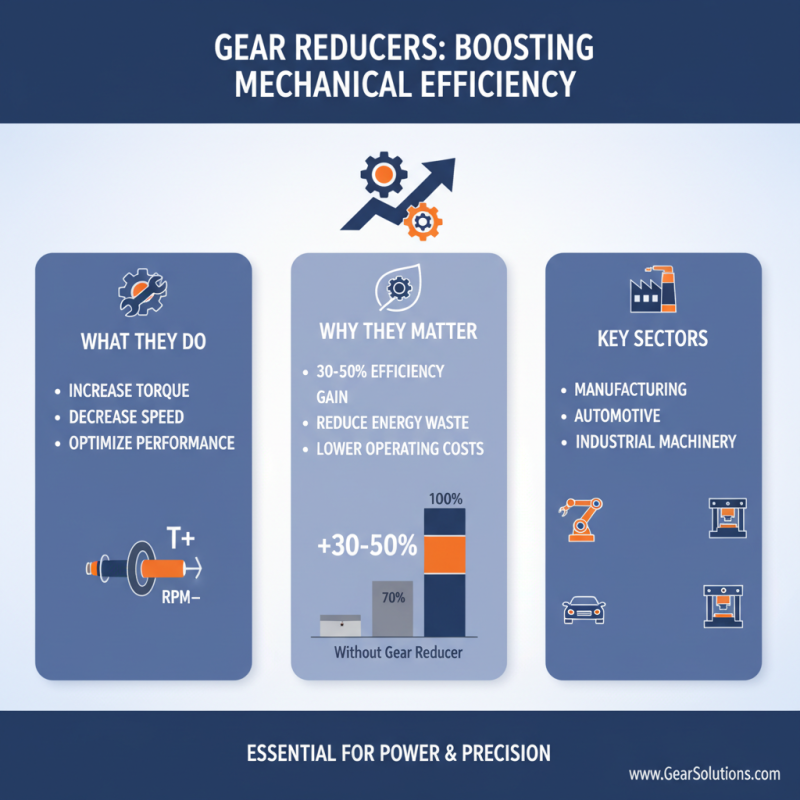
Gear reducers are crucial in mechanical systems. They increase torque and reduce speed for efficiency. This adjustment enhances overall machine performance. According to industry reports, gear reducers can improve efficiency by 30% to 50%. This is significant, especially in manufacturing and automotive sectors. By minimizing energy waste, businesses can cut operating costs.
Many engineers prefer gear reducers because of their durability. They can withstand heavy loads and tough working environments. This resilience contributes to lower maintenance costs over time. In addition, gear reducers can be tailored to different applications. Customization allows for optimization in various systems, enhancing productivity.
**Tip:** Regularly check lubrication levels in gear reducers. Proper lubrication can extend life and performance.
Despite their advantages, gear reducers must be chosen carefully. Not all systems require the same specifications. Over or under-sizing can lead to inefficiencies. This often results in unexpected downtime. Understanding your machine's requirements is essential for best results.
Related Posts
-

Exploring Innovative Applications of Induction Motors Across Different Industries
-

How to Choose the Right Gear Reducer for Optimal Efficiency: A Guide for Global Buyers
-

How to Choose the Right Pump Motor for Your Application
-

Why Is an Electric Motor Essential for Modern Technology?
-

2025 How to Choose the Right Mining Motor for Your Operations
-
How to Choose the Right RV Gearbox for Your Vehicle Performance
-

Phone
Phone

0086-13586199782
-
E-mail
-

Whatsapp
-

Wechat
Wechat

-

Top
