
Top Electric Motor Types and Their Applications Explained?
Electric motors are a crucial component in modern technology. They power a multitude of devices, from household appliances to industrial machinery. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the electric motor market is expected to reach $224 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.3%. This rapid growth showcases the importance of understanding different types of electric motors and their applications.
Different motor types, including AC, DC, and stepper motors, serve various industries. Electric motors provide energy efficiency and reliability. In manufacturing, they drive conveyor belts, pumps, and fans. In transportation, electric motors are increasingly used in electric vehicles (EVs). However, despite their advantages, not all applications are suited for electric motors.
Choosing the right motor type can be complex. Factors include power requirements, duty cycles, and environmental conditions. Imperfect choices can lead to inefficiencies, costly downtime, and even safety hazards. As technology advances, the need for innovation continues to grow. Understanding electric motors is essential for optimizing performance in an increasingly electric world.
Overview of Electric Motor Types and Their Characteristics
Electric motors are essential components in numerous industries. Understanding their types can optimize their use. There are several electric motor types, each with unique characteristics. Common types include brushed DC motors, brushless DC motors, and induction motors. Each has specific advantages and limitations.
Brushed DC motors are simple and cost-effective. They are easy to control and widely used in small appliances. However, they wear out faster due to brush friction. A report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) states that around 40% of all electric motor applications use brushed designs. This indicates a significant reliance on this type despite its downsides.
Brushless DC motors provide higher efficiency and longer lifespans. They are used in applications requiring precision, such as robotics and drones. Yet, they can be more complex and expensive to manufacture. Induction motors, on the other hand, are sturdy and reliable, commonly found in industrial applications. However, they may not offer the same efficiency as their predecessors. The global electric motor market was valued at approximately $121 billion in 2021, with an expected growth rate of 6% annually, reflecting the continued importance of advancing these technologies.
Top Electric Motor Types and Their Applications
Induction Motors: Principles and Common Applications
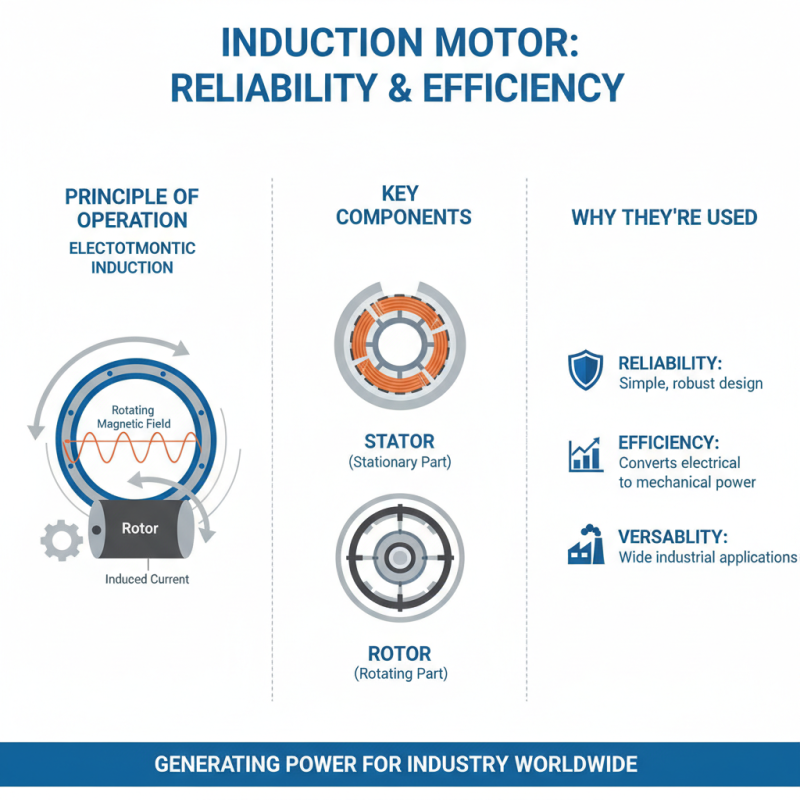
Induction motors are widely used in various industries due to their reliability and efficiency. These motors operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, making them an attractive choice for many applications. They consist of two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator generates a rotating magnetic field, which induces current in the rotor. This process allows the rotor to turn, providing mechanical power.
Common applications of induction motors include HVAC systems, conveyor belts, and pumps. In HVAC systems, they drive fans that circulate air effectively. In manufacturing, they power conveyor belts that transport materials from one point to another. Pumps also rely on these motors to move fluids in various settings, from water treatment plants to agricultural irrigation.
While induction motors are popular, there are challenges to consider. Their efficiency can drop significantly at low loads. This inefficiency can lead to unnecessary energy consumption. Additionally, they can produce vibrations and noise under certain conditions, leading to operational concerns. Understanding these drawbacks is crucial for making informed choices in motor applications.
Synchronous Motors: Features and Use Cases
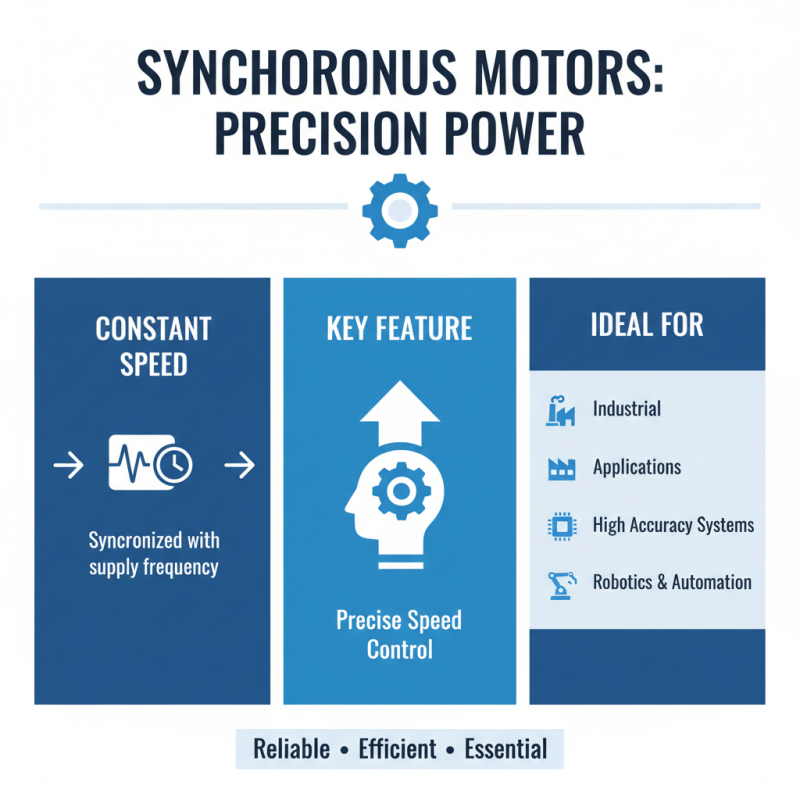
Synchronous motors are vital in various industries. They operate at a constant speed, synchronizing with the supply frequency. This feature makes them ideal for applications requiring precise speed control. Industries in need of such accuracy often rely on these motors.
In manufacturing, synchronous motors power conveyors and pumps. They handle heavy loads efficiently, ensuring optimal productivity. Their ability to run in harmony with energy sources is beneficial, especially in renewable energy applications. However, they can be complex to control, which may lead to operational challenges.
Synchronous motors also find use in large fans and compressors. Their robustness in demanding environments makes them a preferred choice. Still, the initial setup can be a hurdle. Maintenance and technical support are critical for sustained performance. Proper training for operators is essential to maximize the benefits of these motors.
Brushless DC Motors: Benefits and Typical Implementations
Brushless DC motors have gained popularity due to their efficiency and reliability. They operate without brushes, which reduces mechanical wear. This design leads to longer lifespans and less maintenance. Many industries value these features.
In applications like drones and electric vehicles, brushless DC motors shine. They provide smooth and controlled movements. Their ability to deliver high torque at low speeds is essential for these technologies. However, there are challenges. The initial cost can be higher, and designing the controller needs expertise.
Despite these hurdles, the advantages often outweigh the drawbacks. The quiet operation of brushless motors is appealing in residential areas. They also perform well in robotics. However, finding the right size and power rating is crucial. Designers must consider these factors carefully.
Stepper Motors: Functionality and Areas of Use
Stepper motors are unique and versatile. They operate by dividing a full rotation into multiple steps. This precise movement is crucial in many applications. Common uses include 3D printers, CNC machines, and robotics. They allow for accurate positioning and smooth control.
In 3D printing, stepper motors help to achieve fine details. Each tiny movement must be exact. This level of control can drastically affect the final product's quality. In CNC machines, they enable complex shapes and designs. However, too much load can lead to missed steps. This can cause significant errors in the machining process.
**Tips:** When using stepper motors, ensure proper calibration. This helps to avoid inaccuracies. Also, consider the power requirements carefully. Underpowered motors can struggle, causing poor performance.
Top Electric Motor Types and Their Applications Explained
| Motor Type | Functionality | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stepper Motor | Provides precise control of angular position | 3D printers, CNC machines, robotics | High precision, excellent torque at low speeds |
| DC Motor | Converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy | Electric toys, small appliances, power tools | Simple control, wide availability |
| AC Induction Motor | Uses alternating current to create magnetic fields | Industrial machinery, fans, pumps | Robust, low maintenance |
| Brushless DC Motor | Uses electronic controllers to drive a rotating magnetic field | Electric vehicles, drones, computer fans | High efficiency, long lifespan |
| Synchronous Motor | Rotates at a speed synchronized with the supply frequency | Large industrial applications, timing applications | High speed, good power factor |
Related Posts
-
Rising Above Tariff Challenges: How China's Best Electric Motor Manufacturers Thrive
-
10 Advantages of Choosing the Best Break Motor for Your Next Project
-

How to Choose the Right Electric Motor for Your Specific Needs
-

Why Do Electrical Fan Motors Overheat and How to Fix It?
-

Why Is an Electric Motor Essential for Modern Technology?
-

Empowering Your Operations: Discovering Benefits of 3ph Electric Motors for Global Sourcing
-

Phone
Phone

0086-13586199782
-
E-mail
-

Whatsapp
-

Wechat
Wechat

-

Top
