
How to Choose the Right Low Speed Motor for Your Project?
Choosing the right Low Speed Motor can make or break a project. According to John Smith, a leading expert in the motor industry, "Understanding your requirements is key to selecting the correct motor." His insight highlights the importance of clarity in your needs.
In many projects, the specifics can be overwhelming. What torque or speed do you need? Every choice impacts performance. A Low Speed Motor might provide the necessary torque but could complicate installation. Understanding dimensions and weight is crucial.
Many overlook the importance of efficiency. A poorly selected motor may consume too much energy. This not only raises costs but also affects reliability. Experience teaches that a second look can save time and money. Balancing your project's requirements with motor specifications can be challenging. Yet, taking the time to reflect on each detail pays off in better outcomes.
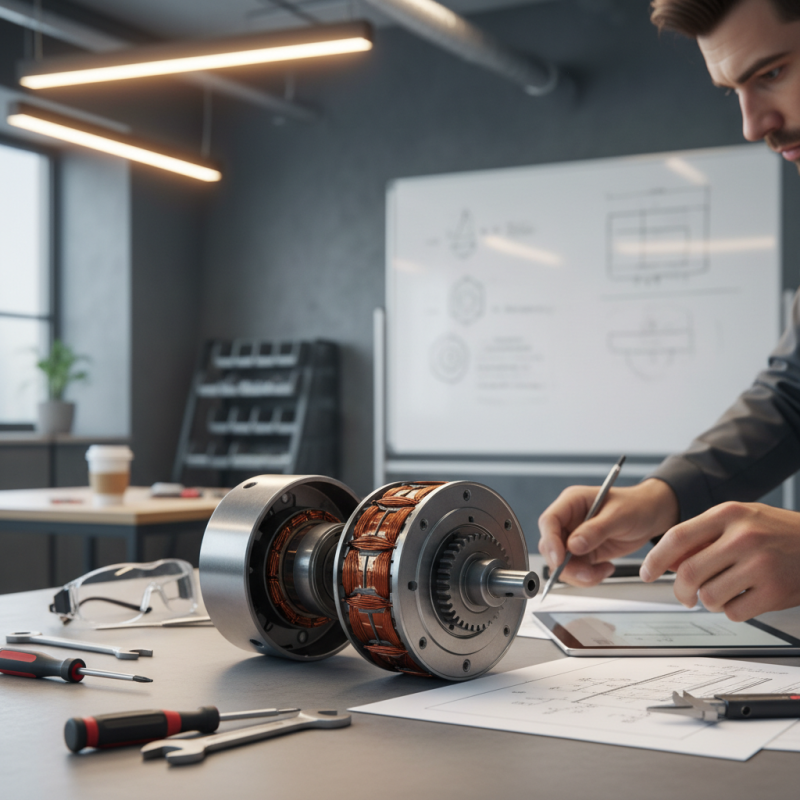

Understanding the Basics of Low Speed Motors
Low speed motors play a crucial role in various applications, from industrial machinery to household appliances. Understanding the basics of these motors helps in making an informed choice for your project. According to industry reports, low speed motors generally operate at speeds below 600 RPM. They are often used in conveyor systems, mixers, and fans due to their efficient torque delivery.
Key considerations include power output and efficiency. Most low speed motors have a high torque-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for heavy loads. For instance, a report from the International Electro-Technical Commission indicates that a well-selected motor can improve energy efficiency by up to 30%. However, determining the right specifications can be challenging. It often requires trial and error, as well as understanding the specific load requirements of your application.
In addition, motor size and cooling methods must be considered. Low speed motors tend to generate more heat, which needs effective management. Parameters like ambient temperature and duty cycle directly influence motor performance. Miscalculating these can lead to underperformance. Thus, it's essential to balance motor size with the intended application to avoid costly mistakes. Keep these factors in mind as you explore options for your next project.
Identifying Key Requirements for Your Project
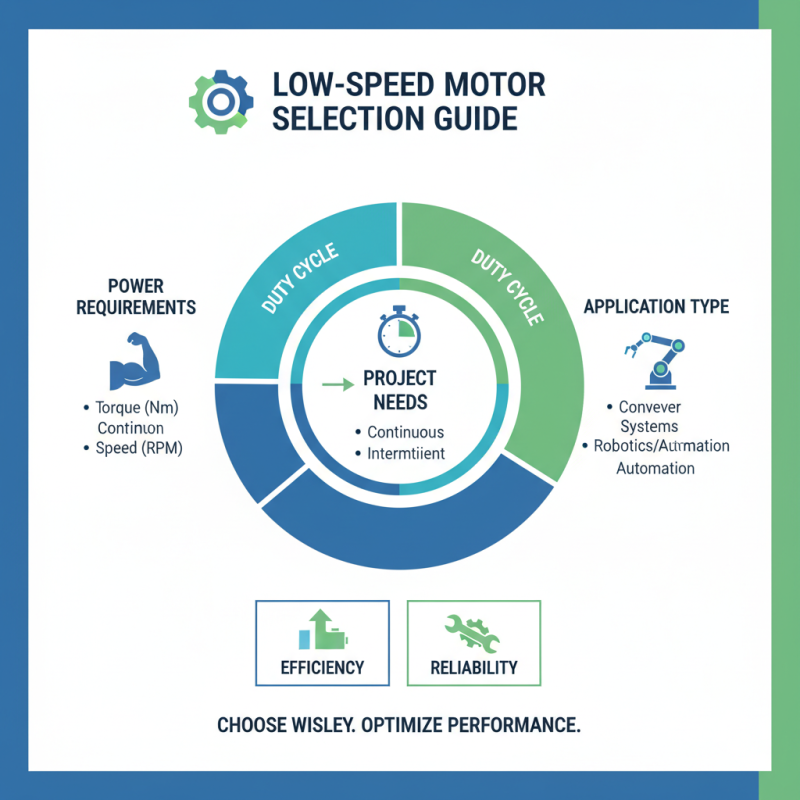
Choosing the right low speed motor requires careful consideration of project requirements. Think about the power needed for your application. It’s essential to know the torque and speed specifications. For instance, a motor designed for continuous use may differ from one aimed at short bursts of energy. Keep these factors in mind as you explore options.
Next, consider the environmental conditions. Will the motor be exposed to dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures? Such factors can significantly impact performance. A motor that works well in a lab may fail in a factory. Reflect on your project's specific conditions. Don’t overlook this detail; it could save you from headaches later.
Budget constraints are another important aspect. Sometimes the cheapest option isn't the best choice. Investing in a reliable motor may provide long-term savings. However, weigh the cost against the features. Aim for a balance that meets your project's needs without overspending. Always revisit your choices as your project evolves. Adjust your requirements if necessary.
Comparing Different Types of Low Speed Motors
When selecting a low-speed motor, understanding the various types is key. You might come across brushed DC motors, which are easy to control and inexpensive. However, they require regular maintenance and can wear out quickly. For some projects, this might not be ideal. Brushless DC motors are another option. They are more efficient and have a longer lifespan, but can be more complex.
Another type is stepper motors. These motors provide precise control for applications that require accurate movement. They are often used in robotics and 3D printers. Yet, they consume power continuously, which might not suit energy-efficient designs. Alternatively, gear motors combine low-speed operation with high torque, making them perfect for heavy-duty applications. Still, their larger size might be a limitation in compact spaces.
Assessing your project's specific needs will guide you in choosing the right motor. Think about speed control, torque requirements, and the space available. Reflecting on potential drawbacks and compromises is essential in this selection process. It takes time and sometimes multiple trials to find the best fit.
Comparing Different Types of Low Speed Motors
This chart compares the torque and efficiency of different types of low speed motors commonly used in various projects, including Gear Motors, Stepper Motors, and DC Motors.
Evaluating Performance Specifications and Efficiency
When evaluating low speed motors, performance specifications are critical. Key factors to consider include torque, speed, and power ratings. According to industry research, low speed motors typically operate between 1 to 500 RPM. The torque output can range from 5 to 50,000 Nm. These specifications determine how effectively a motor can handle the intended load.
Efficiency is another vital aspect. A motor with high efficiency reduces energy consumption, saving costs in the long run. Data shows that efficient motors can achieve efficiency ratings above 90%. However, achieving such efficiency often requires a balance between performance and initial investment. In some cases, cheaper motors offer lower efficiency, leading to higher operational costs over time.
Choosing a suitable low speed motor isn't just about finding one within the specifications. The application context is equally important. It’s essential to assess environmental factors like temperature and humidity. Incorrect motor choice can lead to performance issues. Thus, performance specifications and efficiency must align with specific project needs.
Making the Right Choice: Selecting a Supplier and Model
When selecting a supplier for low-speed motors, various factors come into play. The quality of the manufacturer is crucial. According to industry data, over 70% of performance issues can be traced back to a poor supplier. Reliability is paramount, especially in projects requiring consistent machine operation. A reliable supplier ensures that their motors meet specified standards and performance metrics.
Consider the specifications of the motor. It's essential to match the motor's capabilities with the project's requirements. Look for motors with efficiency ratings above 85%. Studies show that higher efficiency can reduce operational costs significantly. Also, assess the supplier's delivery and support services. Fast response times can prevent delays during critical project phases. However, it's worth noting that not all suppliers adhere to their delivery promises.
Price is often a dominating factor. But a lower price does not always mean a good deal. In fact, 60% of engineers report regretting their choice due to hidden costs associated with cheap motors. These can arise from frequent maintenance or replacements. Selecting the right model relies on careful assessment of not just the price, but also the overall value it brings to your project.
Related Posts
-

Top Strategies for Sourcing the Best Low Speed Motor Innovatively and Cost Effectively
-
7 Excellent Benefits of Using Low Speed Motors for Your Business
-

Discover Premium Low Speed Motors Directly from China's Leading Manufacturing Factory
-

A Comprehensive Comparison of Low Speed Motors Versus High Speed Motors
-

Top 10 Low Speed Motor Manufacturers from China at the 137th Canton Fair
-
How to Choose the Right Centrifugal Pump Motor for Your Applications
-

Phone
Phone

0086-13586199782
-
E-mail
-

Whatsapp
-

Wechat
Wechat

-

Top
