
How to Choose the Right Air Compressor for Your Needs and Applications
When it comes to selecting the right air compressor for your specific needs and applications, understanding the various options available can be a daunting task. Air compressors serve as versatile tools utilized across numerous industries, from automotive repair to construction and home improvement projects. Their primary function is to convert power into potential energy stored in compressed air, enabling users to operate different pneumatic tools efficiently. However, not all air compressors are created equal; the right choice largely depends on the intended use, required power output, portability, and other features that cater to particular tasks.
As you embark on the journey of choosing an air compressor, it's essential to consider key factors such as the required pressure, flow rate, and the overall environment in which the compressor will be used. Understanding these parameters can make a significant difference in selecting a model that meets your demands effectively. Additionally, with a variety of types and sizes available, from small portable compressors to larger stationary units, having a clear understanding of your specific applications will aid in making an informed decision. This guide will assist you in navigating the complexities of air compressor selection, ensuring you find the perfect match for your needs.
Understanding the Different Types of Air Compressors Available
When selecting the right air compressor for your needs, it is essential to understand the various types available and their specific applications. Air compressors can generally be categorized into two main types: positive displacement and dynamic compressors. Positive displacement compressors, such as reciprocating and rotary screw compressors, are well-known for their ability to deliver a consistent supply of compressed air, making them ideal for manufacturing and maintenance tasks. In contrast, dynamic compressors, including centrifugal compressors, are more suitable for high-volume applications such as power generation and large-scale HVAC systems.
According to a report by the International Energy Agency, industrial air compressors account for roughly 10% of energy used in manufacturing. This underscores the importance of choosing an efficient model tailored to your operational requirements. For instance, if your application involves intermittent use, a portable compressor may be more advantageous as it can be easily relocated and operated only when needed.
**Tips:** Always consider the CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) required for your tools or processes—this is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Additionally, evaluate the duty cycle, which indicates how long the compressor can run before needing a cool-down period. Selecting the correct air compressor not only enhances productivity but also has significant implications for energy efficiency and operational costs.
Identifying Your Specific Air Compressor Needs and Applications
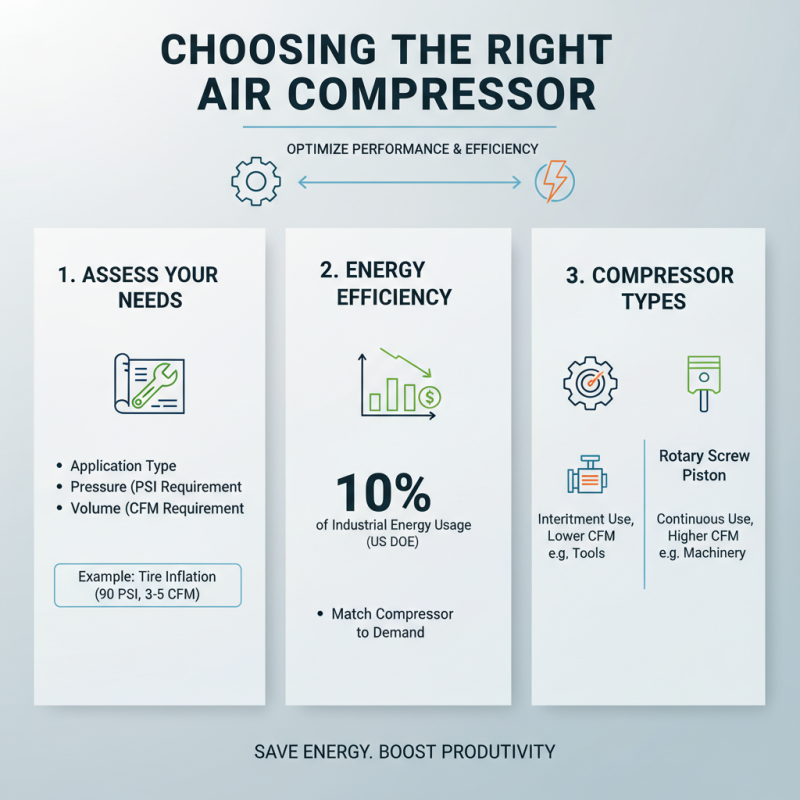
When selecting an air compressor, understanding your specific needs and applications is crucial for optimal performance and efficiency. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, compressed air typically constitutes about 10% of the energy usage in industrial facilities, making it imperative to choose the right compressor that matches your demand. Different applications require different pressure and volume capacities; for instance, inflating tires or powering pneumatic tools may require lower pressures compared to spraying paint or operating high-demand machinery.
Furthermore, assessing the application requirements can significantly influence the compressor size and type. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) states that applications needing continuous air flow typically benefit from rotary screw compressors, which can operate efficiently over extended periods. On the other hand, for intermittent or light-duty tasks, reciprocating compressors are often more suitable, providing flexibility at a lower initial investment. Understanding the specific air requirements—in terms of both CFM (cubic feet per minute) and PSI (pounds per square inch)—is essential to ensure that the selected compressor meets demand without excessive energy costs or equipment wear.
Evaluating Key Specifications and Features of Air Compressors
When choosing the right air compressor, it's crucial to evaluate key specifications that align with your specific needs and applications. The first important specification is horsepower (HP), which indicates the power the compressor delivers. Higher HP often translates to increased air output, making it suitable for heavy-duty tasks such as industrial applications. Conversely, for lighter tasks like inflating tires or running small pneumatic tools, a compressor with lower horsepower may suffice, offering an efficient and cost-effective solution.
Another essential feature to consider is the tank size, measured in gallons. A larger tank allows for longer operation times between refills, which is beneficial for continuous tasks. However, if mobility is a priority, a smaller tank can enhance portability without sacrificing performance. Additionally, air pressure, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), is pivotal. Different applications require varying PSI levels; for example, most nail guns require around 70-100 PSI, while paint sprayers may need higher PSI for optimal results. Lastly, compressor type—oil-lubricated versus oil-free—can affect maintenance and longevity, with oil-free models typically requiring less upkeep while oil-lubricated compressors can provide durability for heavy usage. These considerations ensure you choose an air compressor well-suited to meet your specific operational requirements.
Air Compressor Specifications Comparison
Comparing Portability, Power Sources, and Size Considerations

When selecting the right air compressor, it's essential to evaluate portability, power sources, and size considerations to ensure your choice meets your specific needs. Portable compressors are ideal for individuals who require mobility, whether you're on a job site or working in a home garage. They typically feature lighter designs and wheels for ease of transport; however, they may sacrifice some power compared to larger stationary models. Consider your work environment and frequency of use to determine if a portable option suits you.
When it comes to power sources, air compressors can be powered by electricity, gasoline, or even batteries. Electric compressors are quieter and perfect for indoor use, while gasoline models can provide greater power for outdoor projects. Assess the availability of power sources in your work area and choose accordingly.
Tips: Always check the noise levels of your compressor if you plan to use it in a residential area. Opting for a model with lower decibels can make a significant difference in comfort. Additionally, consider the tank size; a larger tank can provide a more consistent air supply for extended jobs, while a smaller tank is easier to store and transport.
Assessing Budget and Long-Term Maintenance for Air Compressors
When selecting an air compressor, evaluating your budget and considering long-term maintenance are crucial steps that can significantly impact your operational efficiency. According to a report by the Compressed Air and Gas Institute (CAGI), proper budgeting should account for both initial purchase costs and ongoing maintenance expenses, which can comprise up to 30% of the total cost of ownership. This highlights the importance of not just looking for the lowest upfront price but considering the compressor's reliability and durability, as it can save you significant costs in repairs and downtime.
Tips: Always incorporate preventative maintenance strategies into your budget plan. Regular checks and servicing can extend the lifespan of the compressor by 25% or more, according to industry studies. This includes monitoring air filters, checking for leaks, and ensuring proper lubrication, which can prevent expensive repairs and unplanned disruptions in your operations.
In addition to maintenance, the choice of compressor type can also affect your long-term costs. A rotary screw compressor, while initially more expensive, often requires less frequent maintenance and has a longer lifespan than its reciprocating counterparts. Data shows that a rotary screw compressor can operate for 50,000 hours before needing major repairs, compared to just 20,000 hours for reciprocating models. Therefore, considering the operational demands and volume of use can lead to more informed financial planning over the compressor's lifespan.
How to Choose the Right Air Compressor for Your Needs and Applications
| Air Compressor Type | PSI Range | CFM Rating | Price Range ($) | Maintenance Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Electric | 90 - 150 | 2.0 - 4.0 | 150 - 500 | Annual |
| Stationary Electric | 100 - 175 | 4.0 - 7.0 | 500 - 1500 | Semi-annual |
| Gas-Powered | 90 - 150 | 5.0 - 10.0 | 300 - 1000 | Annual |
| Oil-Free | 100 - 125 | 1.5 - 3.0 | 200 - 800 | Annual |
| Heavy-Duty Industrial | 100 - 200 | 10.0 - 20.0 | 2000 - 5000 | Quarterly |
Related Posts
-

5 Effective Tips to Maximize Efficiency of Your Air Compressor for Optimal Performance
-

Exploring Air Compressor Innovations: Insights from the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-

What is an Aluminum Motor and Why is it Essential for Modern Machinery
-

Understanding How Gear Reducers Improve Efficiency in Modern Machinery
-
Exploring Single Phase Ac Motor Trends at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Unlocking Efficiency: The Ultimate Guide to Frequency Converters in Industrial Applications
-

Phone
Phone

0086-13586199782
-
E-mail
-

Whatsapp
-

Wechat
Wechat

-

Top
