
How to Choose the Right Pump Motor for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate pump motor is a critical step in optimizing system performance across various industrial applications. According to a report from the U.S. Department of Energy, motors account for approximately 65% of industrial electricity consumption, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right pump motor to maximize energy efficiency and operational reliability. Inefficient motor selection can lead to increased energy costs and suboptimal performance, highlighting the need for meticulous consideration of technical specifications, application requirements, and environmental conditions.
Moreover, the global pump motor market is projected to grow steadily, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions. Research indicates that the size of the pump motor market is expected to reach over $4 billion by 2025, reflecting the significance of this component in driving industrial productivity. This growth underscores the importance of understanding motor types, power ratings, and matching them effectively with pump designs. By making informed decisions when selecting a pump motor, organizations can enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and contribute to sustainable practices in their respective industries.

Understanding Pump Motor Types: AC vs. DC Motors in Applications
When selecting a pump motor for your application, understanding the differences between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) motors is crucial. AC motors are commonly used due to their simplicity and durability. They tend to be more efficient in larger applications, offering a consistent power supply without the need for complex controllers. Moreover, AC motors generally require less maintenance and are often more cost-effective in the long run, making them a reliable choice for industrial settings.
On the other hand, DC motors provide advantages in terms of speed control and torque generation. Offering greater flexibility, they are ideal for applications where precise speed and torque adjustments are necessary. This makes them well-suited for smaller or more specialized pumping tasks. However, DC motors tend to require more maintenance because of their internal components, like brushes, which can wear out over time. In situations where variable speed is essential or where space is limited, a DC motor may be the better option, despite potentially higher operational costs. Understanding these distinctions can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of your pumping system.
Key Factors to Consider: Power, Speed, and Efficiency Ratings
When selecting the appropriate pump motor for your specific application, focusing on power, speed, and efficiency ratings is essential.
Power is a fundamental factor that directly affects the performance of the pump.
It is crucial to match the motor's power output with the requirements of the pump system to ensure optimal functionality.
Insufficient power can lead to inadequate flow rates and performance, while excessive power may cause undue wear and increased energy costs.
Carefully evaluating the horsepower needs of your application will help in determining the right fit.
Speed is another critical element to consider, as it influences both the pump's flow rate and the pressure generated.
Depending on the application, different speeds may be required to achieve the desired results.
For example, high-speed motors can provide quick flow rates for specific tasks, while lower speeds can be more suitable for applications requiring more controlled flow.
It is advisable to examine the pump's design and the system's requirements to establish the most effective motor speed.
Lastly, efficiency ratings play a pivotal role in determining long-term operational costs.
Electric motors with higher efficiency ratings can significantly reduce energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills and reduced environmental impact.
By prioritizing energy-efficient motors, you can achieve optimal performance while promoting sustainability in your pump applications.
Evaluating these three key factors—power, speed, and efficiency—will enable you to make an informed decision when selecting the right pump motor for your needs.
Matching Motor Specifications with System Requirements and Load Types
Selecting the appropriate pump motor for a specific application involves a detailed understanding of motor specifications in relation to system requirements and load types. The first step is to consider the operational conditions, including fluid type, operating temperature, and pressure ranges. A 2022 industry report by the Hydraulic Institute indicates that nearly 40% of motor failures stem from mismatched motor specifications, underscoring the criticality of aligning motor capabilities with operational demands. For example, if the pump system operates under variable load conditions, a motor with a variable frequency drive (VFD) could enhance efficiency by adjusting to changing loads.
Next, load type must be carefully analyzed to ensure compatibility with motor performance. Different applications may experience varying degrees of torque and load fluctuation. A study published in the Journal of Mechanical Engineering found that improper sizing of motors to specific load types can lead to up to a 30% decrease in potential operational efficiency. Therefore, understanding whether the load is continuous or intermittent, and its impact on motor selection, is essential. Matching the motor’s torque characteristics with those of the application will not only preserve motor life but also improve overall system efficiency, resulting in significant energy savings and reduced operational costs.
Evaluating Environmental Conditions: Temperature, Humidity, and Vibration
When selecting the right pump motor, it is crucial to evaluate the environmental conditions in which the motor will operate. Temperature can significantly affect the performance and longevity of the motor. High temperatures can lead to overheating, reducing the efficiency and potentially causing premature failure. It is essential to choose a motor rated for the highest expected ambient temperature of the operating environment. Conversely, in low-temperature conditions, motors may require additional considerations such as lubrication changes or heating elements to maintain optimal performance.
Humidity is another critical factor that needs attention. Elevated humidity levels can cause corrosion and electrical failures due to moisture ingress. It is advisable to select motors with appropriate protective coatings and sealing methods to guard against moisture-related damage. Additionally, the presence of vibration in the operational setting can contribute to mechanical wear and structural failures. Motors should be mounted securely with adequate vibration dampening solutions to minimize stress on the components. By addressing these environmental factors, you can ensure more reliable and efficient motor operation tailored to specific application requirements.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs. Long-term Operational Expenses
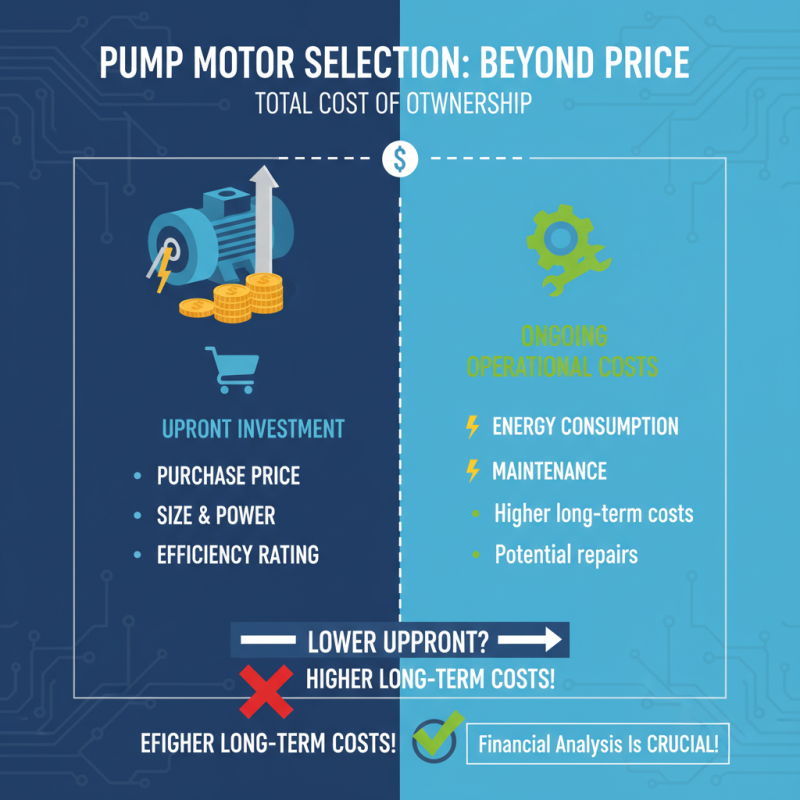
When selecting a pump motor, the financial implications extend beyond the initial purchase price. It is crucial to conduct a thorough cost analysis that considers both the upfront investment and ongoing operational expenses. The initial cost of a pump motor can vary significantly based on factors such as size, power needs, and efficiency ratings. While it may be tempting to choose a lower-cost option, doing so may result in higher long-term operational costs, particularly in terms of energy consumption and maintenance requirements.
Operational expenses encompass energy costs, which can be substantial depending on the motor's efficiency. Energy-efficient motors may have a higher upfront cost, but they often provide savings over time by reducing electricity bills. Additionally, maintenance and repair costs play a critical role in overall expenses; motors that are built for durability and reliability are less likely to incur frequent repair expenses. Thus, conducting a comprehensive cost assessment that includes these long-term implications will lead to better decision-making, ensuring that the selected pump motor not only meets immediate operational needs but also proves to be economical over its lifespan.
Related Posts
-

Maximize Your Global Sourcing: Discover Cutting-Edge Centrifugal Pump Motors at the 2025 Canton Fair
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Electrical Fan Motor for Your Home
-

Maximize Efficiency with Exceptional After Sales Support for the Best Industrial Motor
-

Exploring Air Compressor Innovations: Insights from the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-

Empowering Global Industries: Quality Frequency Converters from China's Leading Manufacturers
-

Future Trends in the Best Iron Body Motor Market Towards 2025
-

Phone
Phone

0086-13586199782
-
E-mail
-

Whatsapp
-

Wechat
Wechat

-

Top
