
What is an AC Electric Motor and How Does It Work?
An AC Electric Motor is a crucial component in modern machinery. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. This process is fundamental in various applications, from household appliances to industrial machines.
Understanding how an AC Electric Motor works offers insights into its efficiency and functionality. These motors operate on the principles of electromagnetic induction. They can vary in size and power, impacting their applications. Some are small and used in fans, while others are large for industrial machines.
However, not all AC Electric Motors are perfect. Efficiency can decline over time due to wear and tear. Some designs may produce unwanted noise or vibration. Reflecting on these limitations can lead to better designs and improvements in the future.
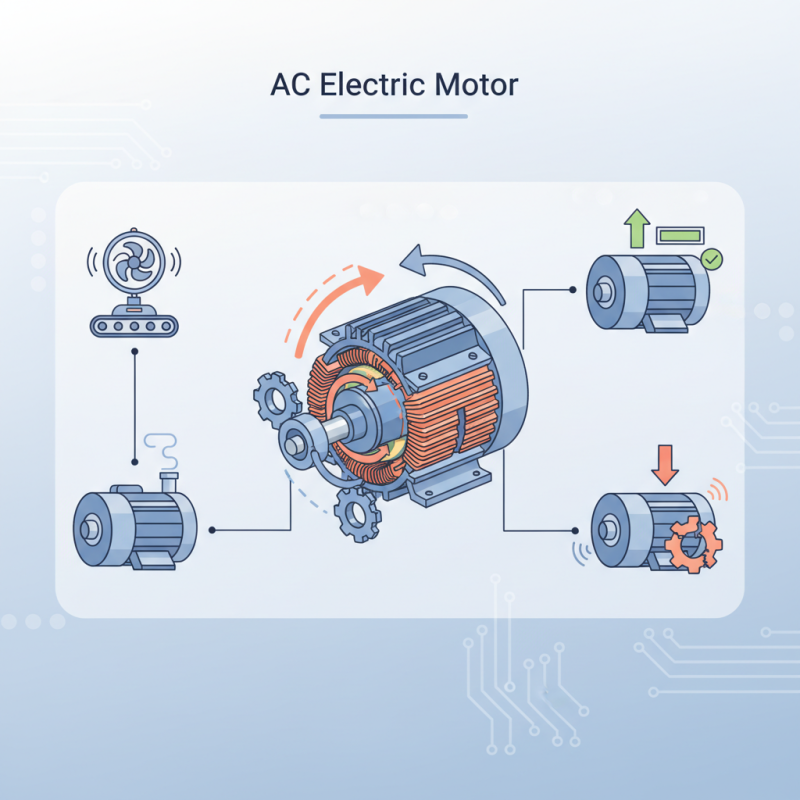
What is an AC Electric Motor?

An AC electric motor is a type of electric motor that runs on alternating current (AC). It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Unlike DC motors, AC motors do not require commutation; their operation is simpler. They consist of a rotor and a stator. The stator creates a rotating magnetic field that induces current in the rotor. This can create torque and produce motion.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), in 2023, AC motors account for approximately 70% of global industrial motor sales. Industries rely heavily on these motors due to their efficiency and simple design. Various applications include fans, pumps, and conveyors. The efficiency of AC motors often exceeds 90%, reducing energy consumption significantly. However, the initial cost can be higher, which may deter some users.
Despite their efficiency, AC motors have limitations. For instance, they can be less effective at low speeds. This leads to energy losses, requiring careful application consideration. Additionally, their performance can be affected by environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity. Understanding these aspects is crucial. Evaluating the benefits and drawbacks can help industries make informed decisions.
The Basic Components of an AC Electric Motor
AC electric motors are essential in many applications. They convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Understanding their basic components can help in maintenance and repairs.
One key component is the stator. This stationary part houses coils of wire. When electrical current passes through these coils, a magnetic field is generated. The rotating part is called the rotor. It sits inside the stator and is free to spin. As the rotor turns, it produces mechanical work. The interaction between the rotor and stator magnetism is crucial.
Tips: Regularly check for wear in the bearings. This prevents unnecessary friction and extends motor life. Also, keep the motor clean. Dust can insulate and reduce efficiency.
Another important feature is the commutator in some designs. It helps direct current. However, it can wear out over time. Users should monitor its condition. Ignoring it may lead to performance issues.
Tips: Listen for unusual sounds. They may indicate internal problems needing attention. Don't delay repairs, as this could worsen the situation.
How AC Electric Motors Generate Mechanical Motion
AC electric motors are fascinating devices that transform electrical energy into mechanical motion. They operate using electromagnetic principles. This conversion process occurs through the interaction of a rotating magnetic field and conductors. As current flows through the motor's windings, it creates magnetic forces. These forces act on the rotor, generating motion.
The beauty of AC motors lies in their simplicity and efficiency. A stator generates a rotating magnetic field, while the rotor spins within this field. The rotor induction happens when the magnetic field interacts with it. This interaction produces torque, propelling the rotor. The speed and direction of motion can be adjusted by changing the frequency of the AC supply, making them versatile.
While AC motors are efficient, they are not without challenges. Overheating can occur if they are overloaded. This can impact performance and lifespan. Additionally, noise and vibration might arise during operations, affecting nearby equipment. Continuous monitoring helps prevent such issues, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the motor. Balancing efficiency and performance remains a critical challenge for users and manufacturers alike.
Types of AC Electric Motors and Their Applications
AC electric motors are classified into two main types: synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous motors operate at a constant speed. They are widely used in applications requiring precise speed control. For instance, they play a crucial role in industrial machinery and high-performance applications. As of 2022, synchronous motors account for about 40% of the global AC motor market, according to industry reports.
On the other hand, asynchronous motors, commonly known as induction motors, are more prevalent. They represent roughly 60% of the AC motor market. These motors are favored for their simplicity and ruggedness. They are widely utilized in fans, pumps, and other equipment. The ease of manufacturing and lower maintenance make them a popular choice. However, their efficiency can be a concern, particularly in variable-speed applications.
The applications of AC motors extend beyond industrial settings. They find uses in residential areas for air conditioning, refrigeration, and pool pumps. The growing demand for energy-efficient solutions drives innovation in motor technologies. A study from a leading market research firm indicates a shift towards smarter, more adaptable AC motors in upcoming years. Despite advancements, issues like energy losses remain a critical consideration for engineers and manufacturers alike.
What is an AC Electric Motor and How Does It Work? - Types of AC Electric Motors and Their Applications
| Type of AC Motor | Description | Common Applications | Efficiency Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synchronous Motor | Runs at a constant speed, synchronized with the supply frequency | Compressors, Pumps, Fans | High |
| Induction Motor | Requires no brushes and runs on electromagnetic induction | Industrial Drives, Conveyors, Lifts | Medium |
| Split Phase Motor | Provides high starting torque; has two windings | Fans, Blow dryers, Washing machines | Moderate |
| Capacitor Start Motor | Uses a capacitor to improve starting torque | Refrigeration, Air conditioning, Small pumps | High |
| Shaded Pole Motor | Simple and inexpensive, low starting torque | Fans, Hairdryers, Small appliances | Low |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using AC Electric Motors
AC electric motors are widely used in various applications, but they come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. On one hand, they offer high efficiency and reliability. These motors can run continuously for long periods with minimal maintenance. Additionally, they can handle large power loads, making them suitable for heavy machinery.
On the downside, AC motors may require a more complex setup. This includes additional components like inverters. These added elements can increase the initial cost and complexity of installation. Moreover, they can be less efficient at low speeds. Over time, this inefficiency may lead to higher energy consumption.
While AC motors thrive in specific environments, they might not be the best choice for every application. The noise levels in some AC motors could be higher than expected. Users should also consider the specific requirements of their projects. Balancing these factors can lead to better decision-making in selecting the right motor.
Related Posts
-

A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding AC Motors for Global Buyers
-
How to Choose the Best Three Phase Ac Motor for Your Industrial Needs
-

Why Choose a Three Phase Ac Motor for Your Applications?
-

Empowering Your Operations: Discovering Benefits of 3ph Electric Motors for Global Sourcing
-
Rising Above Tariff Challenges: How China's Best Electric Motor Manufacturers Thrive
-
Unveiling the Specifications of the Best AC Electric Motor: A Comprehensive Technical Review
-

Phone
Phone

0086-13586199782
-
E-mail
-

Whatsapp
-

Wechat
Wechat

-

Top
